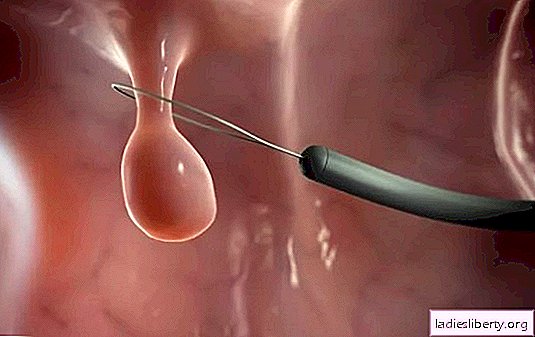
Polyps are benign formations of overgrown epithelial tissue. In the nose, they look like peas, mushrooms or grapes, their sizes vary.
According to statistics, polyps in the nose (polyposis, nasal polyps) are found in 1 - 5% of the world's population. It is found in all age categories (both in children and adults), men are more likely to suffer: they are prone to nasal polyposis about 4 times more. Although these data are contradictory, and according to some data, polyps in the nose, on the contrary, are more often found in women by 2 times than in men.
Polyps in the nose - signs
The formation of polyps in the nose is a kind of compensatory reaction of the body in response to colds and other infectious diseases of the nose.
Epithelial cells of the nasal mucosa sometimes can not cope with the causative agent of infection. There is an activation of leukocytes that destroy the pathogenic microflora, but their number is often not enough to fight the infection.
The body is trying to increase the area of epithelial tissue to successfully fight the infection - as a result of its proliferation, polyps occur:
• mobile painless growths of a round or oval shape;
• diameters from a few millimeters to several centimeters;
• remind a pea or bunch;
• with a smooth surface;
• gelatinous consistency.
Localization distinguishes:
1. Antrochoanal polyps - located in the maxillary sinuses, grow from the upper jaw to the nasopharynx. Mostly they occur in children due to a small transition from the maxillary sinuses to the nasal cavity.
2. Ethmoidal - grow in the sinuses of the sinusoidal tissue, mainly in adults, when examined by ENT - a doctor with expanders, they are clearly visible.
In children, mainly of preschool age, with low and weakened immunity, when the immune system works poorly, body tissues themselves fight infection. As a result, polyps form.
Polyps in the nose - causes
When diagnosing polyps in the nose, the causes of their appearance are associated with chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane. To its appearance lead:
• colds infectious diseases occurring with damage to the nasal mucosa - rhinitis (runny nose);
• chronic rhinitis without adequate treatment, which is caused by a local infection or immunodeficiency;
• chronic inflammation of the paranasal sinuses (PPN) (sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis, rhinosinusitis);
• allergic rhinitis (mainly in childhood);
• some diseases that also have an allergic component (bronchial asthma, intolerance to aspirin, cystic fibrosis, etc.);
• curvature of the nasal septum, obtained mainly as a result of trauma, which as a result of developing difficulty breathing leads to the compensatory development of nasal polyps;
• improper nutrition, which provokes the formation of an increased amount of mucus in the nose, creating favorable conditions for the development of infection, and in the future - polyps;
• genetic predisposition - it is proved that polyps are inherited (with cystic fibrosis).
Polyps in the nose - the first symptoms
In the presence of polyps in the nose, the first symptoms depend on many factors, including the size and prevalence of formations. In cases of small polyps, there may be no clinical symptoms.
Three stages of polyps are distinguished depending on the size of the lesions in the nose:
Stage I - the polyp slightly overlaps the nasal cavity.
Stage II - a substantial part of the nasal cavity is blocked.
Stage III - the entire nasal passage is closed with a polyp.
When large polyps in the nose are reached, the first symptoms appear:
• nasal congestion, obstructed nasal breathing - this is due to the fact that overgrown polyposis formations block part of the nasal passage, in addition, it compresses the blood vessels of the nasal mucosa;
• runny nose, mucous or mucopurulent discharge from the nose: these are signs of secondary infection and increased work of the glands;
• sneezing, which is explained by an increase in the polyp, which in the process of growth touches and irritates the cilia of the mucosa, which perceive it as a foreign object, sneezing is a protective reaction of the body from getting into the nasal cavity and further foreign objects, it does not bring relief in these cases;
• hypoosmia, anosmia (decrease or absence of smell): when the connective tissue grows in the polyp, the receptors that perceive odors are disturbed - air stops flowing to that part of the nose where odor recognition occurs;
• a headache is the result of hypoxia that develops due to impaired breathing through the nose and insufficient oxygen supply to the brain, as well as sinusitis or frontal sinusitis, which are often a chronic, periodically worsening process in the presence of polyps;
• violation of voice, nasal;
• snoring.
With polyps in the nose, the first symptoms in children can be frequent adenoiditis and tonsillitis.
The appearance of the patient, especially the child, is also characteristic:
• constantly open mouth;
• smoothing nasolabial folds;
• change in the shape of the face and dentition;
• breathing through the mouth.
If you have at least one or two of these signs, you must consult a doctor with your child.
Polyps in the nose - treatment
If the diagnosis is verified, polyps in the nose are found, their treatment depends on the cause that provoked their formation. With small sizes of polyps, therapeutic treatment is prescribed.
In case of allergic rhinitis, it is necessary to identify the cause, then antihistamines (Loratadin, Tsetrin, etc.) are used for treatment.
If an inflammatory process (sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, etc.) is detected with polyps in the nose, treatment consists in the appointment of antibacterial drugs (Macropen, Ceftriaxone, etc.).
With nasal polyps caused by aspirin intolerance, berries containing salicylates (strawberries, gooseberries, cherries, currants) are excluded from use, NSAIDs are also unacceptable (they contain salicates).
Topical steroid preparations (fluticasone, beclomethasone, etc.) are used for treatment, which affect exclusively the nasal mucosa. They reduce polyps, the inflammatory process and swelling of the nasal mucosa, but in large doses they have side effects.
Cromoglycates are also used - mast cell membrane stabilizers (sodium cromoglycate, ketotifen, etc.), which have an antihistamine effect and prevent the release of histamine from mast cells.
Immunotherapy - has recently become widespread. Such drugs as Ribomunil are used - it promotes the activation of humoral and cellular immunity, contains bacterial antigens and non-specific immunomodulators, activates the synthesis of specific antibodies to streptococci that increase immunity.
When a patient is treated at a late stage, only surgical treatment is possible: an operation to remove polyps is necessary.
The operation is performed for certain indications:
• the inability to breathe through the nose because of its full stuffiness;
• a sharp decrease in smell and taste;
• frequent attacks of bronchospasm or the appearance of bronchial asthma;
• inflammation of the PPN;
• S - shaped curvature of a high degree of nasal septum of the nose;
• snoring;
• bloody discharge, sometimes with an unpleasant odor.
In addition to endoscopic surgery, there is a laser method for removing the polyp. It is performed on an outpatient basis. A positive point in laser treatment: the sinuses are not opened and polypous tissue is not removed. But it must be borne in mind that there are certain contraindications to laser treatment:
• multiple polyposis;
• pregnancy;
• bronchitis with obstructive component;
• Seasonal flowering of certain plants that can cause allergic rhinitis.
Polyps in the nose - prevention
If polyps in the nose are identified and operated on, prophylaxis consists in examining an ENT doctor twice a year to avoid the re-development of the disease.
You can prevent the disease itself or its relapse by following the following rules:
1. Avoid contact with irritants (dust, tobacco smoke, various chemicals).
2. Constantly monitor the humidity in the room - this will help moisturize the airways and avoid inflammation.
3. Follow personal hygiene and wash your hands thoroughly.
With timely access to a doctor, many diseases can be avoided, including the formation of polyps.