Carnations will enliven any corner in the garden or decorate the balcony with their bright flashes of white, yellow, all shades of purple.
Different types and varieties differ in the timing of vegetation and flowering, the size of the flowers, their terry, shape and color of the petals.
In order for these many-faced flowers to please longer with lush flowering and delicate aroma, it is necessary to adhere to simple rules for growing cloves.
Types and varieties of carnations
The following species are considered the most popular for growing in a summer cottage:
• clove turkish or bearded (D / barbatus) is short (15-20 cm) and tall (60-80 cm). The main characteristic difference from other types of cloves is that its small flowers (simple or double) are collected in "umbrellas" with a diameter of 10-12 cm. Blossoms in June - July. Flowers can be either plain or tricolor. Famous varieties: "Red Monarch", "Diadem", "Newport Pink", "Wiese Riesen", "Kupferrot", "Schneeball", "Mirage".
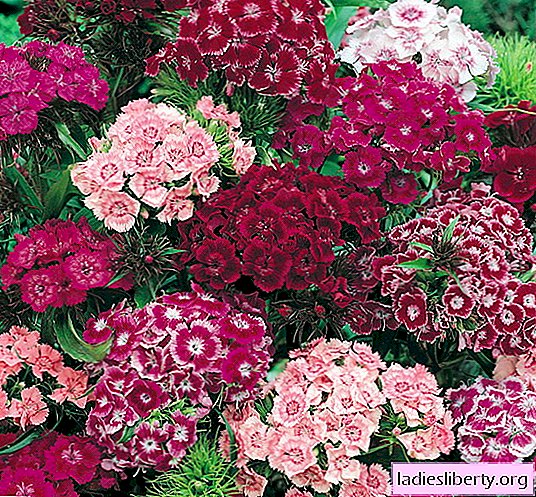

• clove chinese (D / chinensis) is a perennial plant. In Russia, due to climatic features, they are grown as an annual crop. It grows in the form of bushes with a size of 15-50 cm. It blooms from July to August. On dwarf varieties, a contrasting color ring in the center of the flower is characteristic. Popular varieties: "Parfait Strawberry", "Ideal Rose", "Color Magician", "Ideal Rose".
• pinnate carnation (D. plumarius) - a small plant (25-30 cm), forming a dense "pillow" of a large number of shoots. Up to 4-5 years can remain in one place. Flowers can be simple and double, have a pleasant aroma. Coloring varies from all shades of pink to white. Blossom begins in June. Winter hardiness. The most famous varieties are: "Cyclops", "Pheasant's Eye", "Sweetness", "Semi-double Mixed", "Semi-double Mixed".
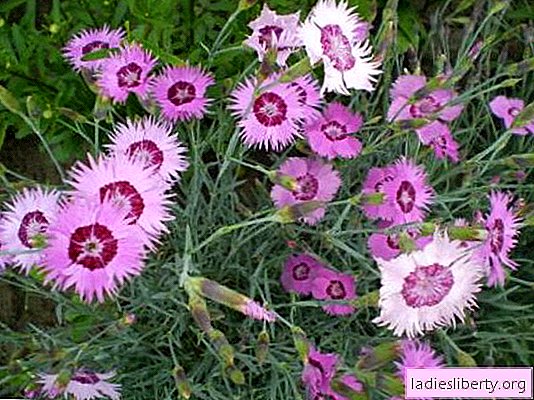

• alpine clove (D. alpinus) - perennial stunted (20-25 cm) species. It is used in rock gardens, rockeries, as a border and groundcover.
• clove grass (D. deltoides) forms loose curtains. Winter hardiness up to -40 ° С. It begins to bloom in late June and until the second decade of September. The most famous varieties: "Brilliancy", "Flashing Light", "Microchip", "Arctic Fire". Planted on alpine slides, in borders, for decorating tree trunks under young fruit trees.
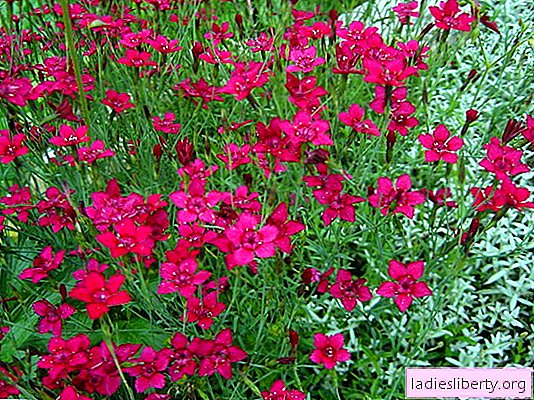

• Dutch or garden cloves (D. Caryophyllus) is grown as a perennial; flowering lasts from May to August. The flowers are double, semi-double, their color is different. Among this species, cloves such as Chabot, Souvenir de Malmaison, Grenadines became popular.

Among garden cloves, a remontant that is blooming many times per season is appreciated. This hybrid was obtained by multiple crosses of different species and forms. Depending on the size of the stems (tall - from 60 cm, medium - 30-60 cm and dwarf - below 30 cm) used for cutting, decorating flower beds, landscaping balconies, as potted plants in indoor floriculture.
Growing cloves: the choice of planting material
You can grow cloves with seeds, seedlings, rooted cuttings, bushes.
Seeds are the cheapest way to purchase planting stock. Perennials grown from seeds will bloom only in the second year.
Seedlings and rooted cuttings can be purchased at nurseries or greenhouses.
Bushes do not appear in mass-market stores. They can be purchased from neighbors in the country.
You need to choose planting material taking into account the climatic conditions of your region and the purpose of using these flowers (in rockeries, alpine hills, for cutting, like a potted crop).
We grow carnations: planting
Landing location: carnations of all kinds to the liking of light sunny areas. Grass, turkish and feathery cloves can grow in partial shade.
Soil: cloves prefer drained fertilized soil with a pH close to neutral. If the location is close to groundwater, then cloves should be planted in elevated flower beds.
Carnations propagate by seeds and vegetatively (cuttings, division of the bush and layering).
One-year-old cloves (Shabo, Chinese) and two-year-old are grown by seeds. However, plants obtained from seeds may not retain varietal color. Sowing is done in January-February in pots with a prepared substrate from leaf soil (2 parts), peat moss (2 parts) and sand (1 part). Seeds are distributed along the grooves (depth 0.3 cm), sprinkled with sand, covered with a film. Crops contain at + 12-16 ° С. After 7-10 days, seedlings appear. During this period, you can use the backlight. When 2 pairs of leaves grow on the seedlings, they are dived into separate cups. To make the bushes compact, pinch the growth point. Seedlings are planted on the beds in the last decade of May or in the first week of June, maintaining a distance between plants of at least 20 cm.
Perennial cloves are sown in the early spring or autumn immediately into the ground. Such plants will bloom only in the second year.
Cuttings propagate all types of cloves, except annuals. Harvesting cuttings is better in early autumn or spring, so that young plants take root before the summer heat or frost. For cuttings need semi-mature developed stems. They are divided into pieces of 3-9 cm in size (the length depends on the type of carnation). Cuttings are best taken from the middle part of the shoot. A cut on the shoot is done under the knot. Two pairs of lower leaves are removed. A sharp knife is cut in depth by 1/3 of the stem between the two lower nodes. Cuttings are planted in a prepared substrate (sand + perlite / vermiculite), covered with a film or placed in a greenhouse until rooting (15-20 days).
Layers grow cloves with long shoots. On the section of the stem between the nodes make an incision of 1/3 of the thickness, bend it to the ground, fix it with sand and water it. After the appearance of the roots, the young plant is separated from the mother and planted separately.
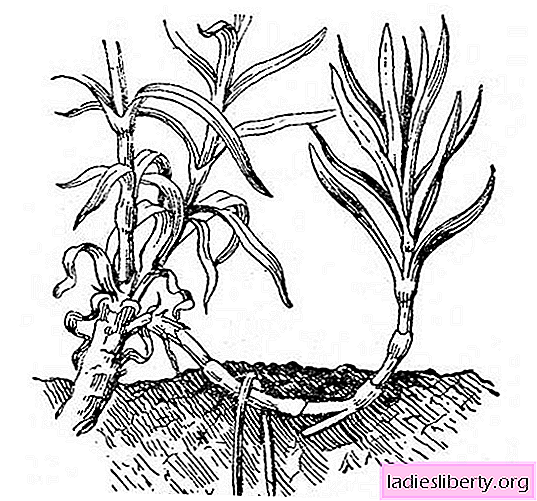

The division of the bush is used for those types of cloves that form sods, and also when it is necessary to rejuvenate a valuable plant variety. The bush is divided into 2-3 years of the growth of the mother liquor. Separated parts bloom in the same year, but not very plentifully.
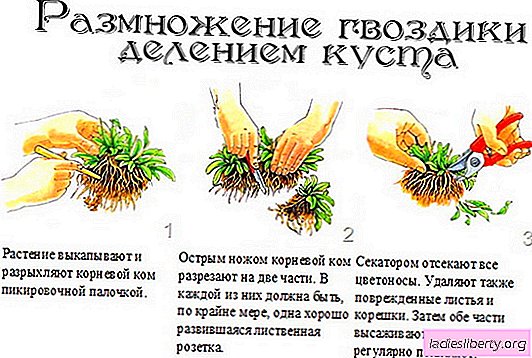
Vegetative propagation is good because in this case, new plants will have all the species characteristics. Carnations, especially perennial ones, should be propagated more often, as over time they lose their decorative effect.
Growing cloves: care
Caring for cloves is simple and consists of watering, weeding weeds, loosening, fertilizing, shelter for the winter.
Watering is carried out 2 times a week in the morning, 12-15 l / m2. Depending on the season, weather and physical properties of the soil, irrigation should be regulated. If the plants are located in the lowlands, then the amount of watering is reduced, otherwise the clove will die on basal rot. Water the flowers under the root, not from above.
After watering, the earth around the plant bushes must be loosened so as not to provoke the development of fungal diseases.
Fertilizers work well on varietal cloves. In autumn, a plot intended for growing cloves is dug with organic fertilizers (humus, peat compost) at a rate of 2 kg / m2. Do not use fresh manure. Cloves need nitrogen to grow foliage, so it is applied (5-6 g / m2) after adaptation of the planted plants in a new place. During tillering and budding, plants are fed with potash and phosphorus fertilizers (4-5 g / m2). You can use complex flower fertilizers, for example, Agricola, Bud, Ideal, etc.
Cloves are resistant to wintering in open ground. In snowless winters, severe frosts (-30-40 ° C) can become dangerous. In the spring, these flowers can also suffer from thaws: sprouts break out on thawed thawed patches, and frost destroys them at night. For safety reasons, you can mulch clove bushes or cover them with fir spruce branches.
Tall varieties must be tied up to avoid breaking the stems.
In summer, to stimulate the appearance of new shoots and secondary flowering, it is necessary to cut off the faded stems.
The main pests and diseases. Methods of dealing with them
Aphid - a dangerous sucking pest that damages young leaves and shoots (they are deformed, become sticky). It multiplies rapidly in dry weather, tolerates viral diseases. Insecticides are used to kill insects.
Thrips - small (1-1.5 mm) sucking insects of brown color. On damaged plants, silver spots form, the growth point is deformed, the flower petals turn brown. To kill thrips, two-time spraying with insecticides is used: Aktara, Fitoverm, Fufanon, Spark with an interval of 4-5 days.

Spider mite and its larvae damage plants by sucking juices from leaves and young shoots. Extensive colorless and dried patches are visible on the damaged leaves. It multiplies rapidly in dry air and high temperature. To kill ticks, it is necessary to use different insecticides and alternate them, as new populations become resistant to poison.
Clove fly - a small insect of brown-gray color and a length of 6-7 mm. Damage is caused by its larvae, which mine the leaves and stems. Part of the shoot over the affected area takes on a gray color, withers and dies. Pest control measures include cleaning and burning of plant debris, plowing or digging sites, thermal disinfection of the soil (in greenhouses). Chemical processing involves the use of insecticides (Karate, Spark, Lightning).
Nematodes affect both the stems and the roots of the plant. Damaged carnations slow growth, leaves turn yellow and dry. With gall nematodes on the roots, swelling and warty growths are characteristic. The fight against it is to disinfect the soil, the use of healthy planting material.
Clove elephant - yellowish-brown beetle with black and white stripes. Lays eggs in the thickness of leaves. Damage to cloves is caused by adults and larvae by eating leaves. Overwinter under plant debris and in the soil. Therefore, autumn digging of the site, cleaning of plant debris, the use of insecticides is mandatory.
Clove leaflet - butterflies measuring 18-22 mm. The female has orange wings, the male has gray-brown wings. Caterpillars do harm: eat leaves and ovaries, braid them with cobwebs, make moves inside the stem.
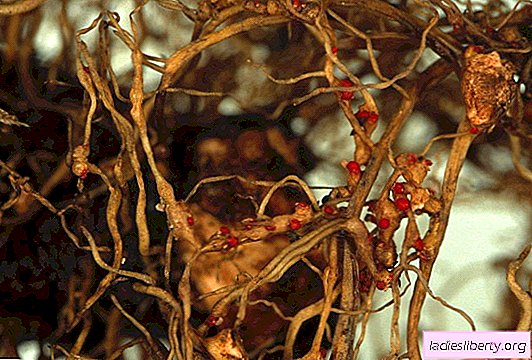
Bacterial cancer - A disease caused by the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens. The growth of diseased cloves is suspended. A characteristic feature of this type of cancer are tuberous growths on the roots. With the development of the disease, the root system rots. Infected plants cannot be treated; they must be burned.
With alternariosis gray spots with a black coating appear on the affected cloves. The stalk bends, new leaves become smaller. The plant withers and dies. The disease develops rapidly with high humidity and soil. The most susceptible to defeat is clove Shabo. It is recommended to alternate crops on the site, destroy plant debris, observe agricultural practices. Sick plants are sprayed with fungicides three times, maintaining an interval between treatments of 10-15 days.

Rust - Another fungal disease. The most dangerous for repairing cloves grown in protected soils. On the affected leaves, stems, buds, orange spots appear with chlorotic areas of adjacent tissues. The disease progresses with increased soil moisture, an overdose of nitrogen and potassium deficiency. At the first sign of rust, plants must be sprayed with fungicidal preparations.

Ring spotting, or mosaic. This disease is mainly affected by Turkish clove. On the cup of the flower and on the leaves it appears in the form of yellow-green elongated rings. The edges of the leaves become wavy and brown, bend. It is recommended to observe agricultural technology and destroy sucking pests - carriers of viral diseases.
Clove phyllophorosis - a fungal disease that affects the vascular system of cloves. Infection occurs through damaged roots. The plant withers, turns yellow, starting from the bottom, and dries. Individual leaves have a reddish color. Damaged brown vessels are visible on a section of the stem. Sick plants are burned; in their place, cloves have not been planted for several years.











