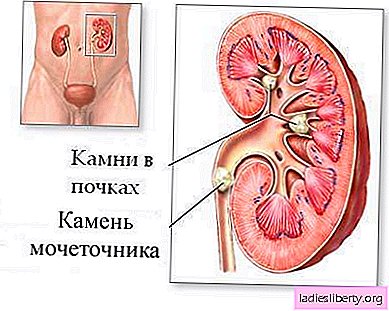
Urolithiasis disease - A disease that is associated with the formation of stones in the organs of the urinary system of a person (most often in the kidneys). The disease affects representatives of all age groups. Only the type of urinary stone usually depends on age.
Urolithiasis - causes
The main cause of urolithiasis is metabolic disorder, especially with regard to changes in the chemical and water-salt composition of the blood. Despite these disorders, the disease cannot develop without the following factors:
- the presence of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, peptic ulcer, colitis) and genitourinary system (prostatitis, pyelonephritis, prostate adenoma, cystitis);
- hereditary predisposition;
- disturbances in the work of the parathyroid glands;
- injuries and bone diseases;
- prolonged dehydration;
- vitamin deficiency (lack of vitamin D is especially critical);
- abuse of spicy, salty, smoked;
- constant use of hard water;
- lack of UV radiation;
- accommodation in a hot climate.
Urolithiasis - Symptoms
Typically, urolithiasis does not go unnoticed. The following characteristic symptoms of urolithiasis are distinguished:
1. Pain in the lumbar region. The pain is unilateral or bilateral, it is characterized by deterioration during physical exertion or when the body position in space changes.
2. Renal colic.
3. Rapid urination and pain during urination.
4. Blood in the urine.
5. Clouding of urine.
6. High blood pressure.
7. Elevated temperature (up to 38 - 40 degrees). This symptom is characteristic for cases when pyelonephritis joins urolithiasis.
Urolithiasis - diagnosis
The current level of development of medicine allows you to diagnose pathological processes associated with urolithiasis in the early stages of development.
The main diagnostic problem is the confidence of many patients in the absence of stones. Most of these patients go to medical institutions with an acute form of urolithiasis, when it is difficult to guarantee the success of the prescribed treatment.
The diagnosis is made by a urologist after examination, conversation with the patient, and also after the following studies:
- general urine analysis;
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the kidneys;
- excretory urography;
- radioisotope nephroscintigraphy.
Urolithiasis - treatment and prevention
First of all, with an acute attack of urolithiasis, it is necessary to remove the symptoms of colic. After this, it is necessary to remove the stones, treat the infectious consequences, and also prevent the re-formation of stones.
Modern medicine offers conservative and surgical methods for removing stones.
With conservative treatment of urolithiasis, stones are removed with the help of special medications, and strict diet and drinking regimen are necessary. This therapy is effective if the patient has small stones (up to 3 millimeters). It should be remembered that the use of such medicines should be constantly monitored by a doctor. In the case of the inflammatory process, it is necessary to additionally carry out antibacterial treatment.
Surgical (or instrumental) treatment of urolithiasis involves surgical intervention, in which the largest stones are removed.
Removal of stones can also be performed by a shock wave, the method is called distance lithotripsy.
A special place in getting rid of urolithiasis is its prevention. It is necessary to significantly reduce the use of fried, fatty, salty and spicy, you can not overeat. In addition, you should drink at least 2 liters of clean water per day. You should also not supercool the lumbar region.